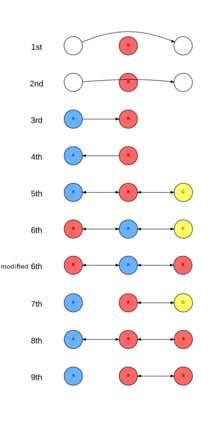
The freedoms of the air are a set of commercial aviation rights granting a country’s to enter and land in another country’s airspace. They were formulated as a result of disagreements over the extent of aviation liberalization in the Convention on International Civil Aviation of 1944, known as the Chicago Convention.
First Freedom – The first freedom is the right to fly over a foreign country without landing. It grants the privilege to fly over the territory of a treaty country without landing.
Second Freedom -The second freedom allows technical stops without the embarking or disembarking of passengers or cargo. It is the right to stop in one country solely for refueling or other maintenance on the way to another country
Third Freedom – The third freedom allows flying from own country to another country to carry passenger, cargo and mail.
Forth Freedom – Flying from another country to own country to carry passenger cargo and mail.
Third and Fourth freedom can be restricted by several factors like capacity of the aircraft, availability of space in airports, airlines having permissions to fly. Normally third and fourth right is granted simultaneously between countries.
Fifth Freedom – The right to fly from between two foreign countries originating or ends in one’s own country. A flight from Melbourne to Kuala Lumpur, with a stop in Jakarta, flown by a Malaysian airline. Passengers and cargo may travel between Melbourne and Jakarta, with no intention to continue to Kuala Lumpur.
Sixth Freedom – The right to fly from a foreign country to another while stopping in one’s own country for non-technical reason. A flight between China to France by Emirates Airline with a stop in Dubai.
The unofficial sixth freedom combines the third and fourth freedoms and is the right to carry passengers or cargo from a second country to a third country by stopping in one’s own country. It can also be characterized as a form of the fifth freedom with an intermediate stop in the operating airline’s home market.
Sixth Freedom – Modified – The right to fly between two places in a foreign country while stopping in one own’s country for non-technical reason. A flight between two Canadian cities by American Airline while stopping in one American city.
The unofficial modified sixth freedom is the right to carry passengers or cargo between two points in one foreign country, while making a stop in the home country.
Seventh Freedom – The right to fly between two foreign countries without a stop in one own’s country. A flight between Spain and Sweden by British Airways.
Eight Freedom – The right to fly inside a foreign country having started or end in one’s own country.
For example, a flight operated by a South African airline between San Francisco and Cape Town, with a full stop in New York. Passengers and cargo may board or disembark the flight in New York, with no intention to board the flight to Cape Town.
The unofficial eighth freedom is the right to carry passengers or cargo between two or more points in one foreign country and is also known as cabotage
Ninth Freedom – The right to fly inside a foreign country without continuing in one’s own country. A flight between Paris and Lyon by Lufthansa.
The unofficial seventh and ninth freedoms are the right to carry passengers or cargo in foreign territories without any service to, from or via one’s own country. The seventh freedom is to provide international services between two foreign countries, and the ninth between points within a single foreign country.
Cabotage is the transport of goods or passengers between two points in the same country by a vessel or an aircraft registered in another country.